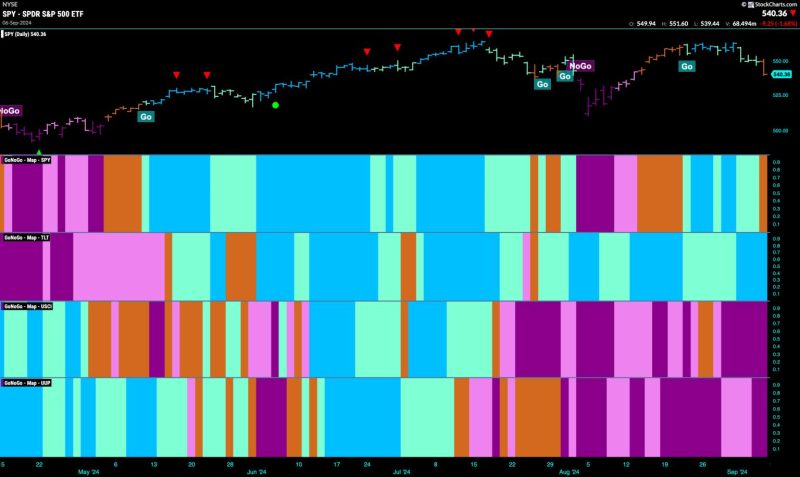
Equities Say Go Fish: How Healthy Are the Markets?
The health of the stock market serves as a barometer for the overall economy, reflecting investor confidence, corporate performance, and broader financial trends. Despite its resilience in the face of various challenges, such as geopolitical tensions, economic uncertainties, and global health crises, the stock market is not immune to volatility and corrections. Assessing the health of the equities market involves examining key indicators and factors that influence its performance.
One of the critical aspects to consider when evaluating the health of the equities market is the price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio. This metric compares a company’s stock price to its earnings per share, providing insights into its valuation. A high P/E ratio may indicate that a stock is overvalued, while a low ratio could suggest that it is undervalued. In assessing the broader market, an elevated average P/E ratio could signal potential risks of a market bubble or unsustainable valuations.
Another key factor in assessing market health is the earnings growth of companies. Strong and consistent earnings growth is generally indicative of a healthy economy and robust corporate performance. Companies with growing earnings are more likely to attract investors and drive stock prices higher, contributing to overall market prosperity. Monitoring earnings reports and projections can offer valuable insights into the health and future prospects of the equities market.
Additionally, monitoring interest rates is crucial in understanding the health of the equities market. Central banks’ monetary policies, particularly changes in interest rates, can have a significant impact on stock prices. Lower interest rates generally stimulate economic growth and lead to higher stock valuations, while higher rates can dampen investor sentiment and decrease stock prices. Keeping track of interest rate movements and their potential implications on stock market performance is essential for investors and analysts.
Market breadth is another important indicator of the equities market’s health. Market breadth refers to the number of stocks participating in a market rally or decline. A broad-based rally with a high number of advancing stocks suggests a healthy and sustainable uptrend, while a narrow rally led by only a few high-flying stocks may be less robust and more susceptible to reversals. Monitoring market breadth can help investors gauge the breadth and strength of market movements, providing insights into potential market conditions.
In conclusion, assessing the health of the equities market requires a comprehensive analysis of various indicators and factors that influence its performance. By monitoring metrics such as price-to-earnings ratios, earnings growth, interest rates, and market breadth, investors can gain valuable insights into market conditions and make informed investment decisions. While market volatility and risks are inherent in investing, understanding the key drivers of market health can help navigate uncertainties and capitalize on opportunities in the dynamic world of equities trading.